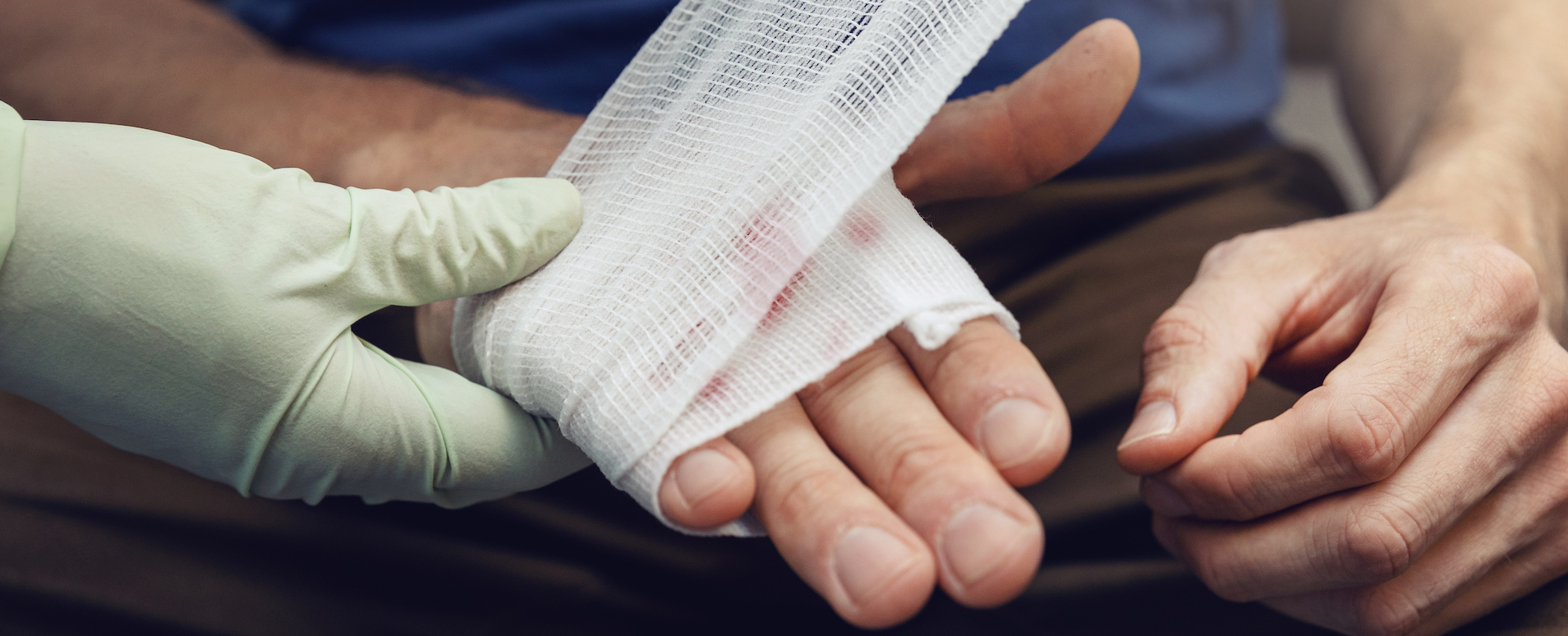
Wounds are a common occurrence in our daily lives, ranging from minor cuts and scrapes to more serious injuries that may require medical attention. Understanding the basics of wounds and the care needed for the different types of wounds is crucial for promoting healing and preventing complications.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what constitutes a wound, types of wounds, methods of wound treatment, and why at-home wound care with skilled nurses can help support optimal healing.
What Are Wounds?
A wound is defined as any injury that disrupts the integrity of the skin, resulting in a break or opening in the tissue. While wounds can vary greatly in severity, they all share the common characteristic of compromising the body’s natural barrier against infection and injury.
Wounds can occur due to a wide range of factors, including accidents, trauma, surgical procedures, or underlying health conditions.
Wounds can limit a person’s independence and leave them feeling vulnerable or unable to participate in normal activities of everyday living. Diligent wound care and holistic support can facilitate healing to ensure that a person can return to their best self as quickly as possible.
In-home wound specialists, like Registered Nurses, are in the best position to take a holistic approach to wound care at home as they seek to nurture and care for a person’s overall well-being.
Types of Injuries That May Require At-Home Wound Care
Incisions
These are clean, straight cuts typically caused by sharp objects such as knives or surgical instruments. Incisions often occur during surgical procedures, where wound care at home after surgery is crucial, or accidents involving sharp objects.
Example: A surgeon makes a surgical incision during a surgery to access and potentially repair a part of the body.
Lacerations
Lacerations are what we think of as normal cuts. They are often time irregular, jagged cuts caused by blunt trauma or accidents. They can result from falls, collisions, or contact with rough surfaces.
Example: A person sustains a laceration after falling and hitting their knee on a sharp edge of furniture.
Abrasions
Also known as a scrape or a graze, abrasions occur when the skin is rubbed or scraped against a rough surface. This results in superficial damage to the outer layer of skin.
Example: A child falls off their bike and sustains abrasions on their knees from skidding along the pavement.
Punctures
Puncture wounds are caused by a sharp object penetrating the skin and underlying tissue. Common examples include stepping on a nail, or an animal bite.
Example: A construction worker steps on a rusty nail at a job site, resulting in a puncture wound to the foot.
Burns
Burns are injuries to the skin and underlying tissue caused by exposure to heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. They are classified into different degrees based on the severity of tissue damage to the point of contact and surrounding tissue areas.
Example: If you spill hot oil on your hand while cooking, that may result in a second-degree burn.
Pressure Ulcers
Also known as bedsores or pressure injuries, pressure ulcers develop due to prolonged pressure on the skin, typically in areas with bony prominences such as the heels, elbows, or buttocks. These can be quick to heal, but those that have difficulty healing and are referred to as chronic pressure ulcers.
Example: An elderly individual confined to a wheelchair develops pressure ulcers on their buttocks from prolonged sitting.
What Is At-Home Wound Care?
After surgery, or when dealing with a difficult wound, a person may require skilled nursing wound care to recover completely. People and their family caregivers often care for the wounds themselves, but professional at-home wound care services are recommended to ensure proper care.
Not only does this take away the stress on the person and their loved ones, but it ensures that the wounds are being carefully observed for signs of infections. This is helpful for people who may be coping with chronic wounds or terminal illnesses.
As a part of wound care at home, skilled nurses monitor patients’ vital signs, ensure timely medication, and assist them with daily activities. Taking vitals is critical as it can indicate infections or loss of blood volume for more extensive wounds and incisions.
Physical assessment information that the nurse gathers will guide the care plan to help keep a person healing at home. Proper wound care after surgery, a one-off accident or for a chronic condition can speed up the recovery process and reduce the wound’s impact on a person’s quality of life.
Methods of Wound Care
The approach to wound treatment varies depending on the type, severity, and underlying cause of the injury. It is also important to note that wound healing may be specific to you and your medical provider, so please note to follow their recommendations. Some common methods of home health would care include:
Cleaning & Debridement
Proper cleaning of the wound is essential to remove dirt, debris, and bacteria that can lead to infection. This often involves gently irrigating the wound with saline solution or mild soap and water. In cases where the wound is contaminated or contains necrotic (dead) tissue, debridement may be necessary to promote healing.
Dressing Changes
Applying an appropriate dressing to the wound may help protect it from further injury. Some dressings are meant to maintain a moist environment conducive to healing, and absorb excess exudate (fluid) from the wound bed. The choice of dressing depends on factors such as the type of wound, its location, the stage of healing, and the preference of your medical team.
Topical Medications
In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe topical wound care medications such as antibiotics, antiseptics, or healing agents to prevent infection, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue regeneration.
These medications may be applied directly to the wound or incorporated into the dressing. It will be important to follow your specific instructions. Please make sure to tell your medical team if you are applying anything else over the counter.
Sutures & Staples
Certain wounds may require closure with sutures (stitches), staples, or adhesive strips to bring the edges of the wound together and facilitate healing. This is commonly done for deep lacerations, surgical incisions, or wounds with clean, straight edges.
Wound sites that have sutures and staples still require cleansing, and may require light dressings on top of them to help prevent rubbing of the staples or sutures on clothes or sheets.
Advanced Therapies
For complex or non-healing wounds, advanced therapies may be needed to promote healing and tissue regeneration. These may include negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), bioengineered skin substitutes, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, the use of leeches, or surgical interventions such as skin grafts or flap reconstruction.
Your nurse will serve as an in-home wound care specialist who can help ensure the right modality of treatment is being followed. They will work closely with your medical team to help provide the recommendations needed to help you heal as quickly as possible.
5 Wound Care Tips for Promoting Healing at Home
1. Keep the Wound Clean
Proper wound hygiene is essential to prevent infection and promote healing. Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after handling the wound. Cleanse the wound gently with mild soap and water or saline solution, and pat it dry with a clean cloth or sterile gauze. You never want to rub or irritate the skin.
2. Protect the Wound
Dressings offer protection for wounds, but they are not always recommended. If appropriate, dressings or a bandage over the wound can keep it protected from dirt, bacteria, and further injury. If you do use a bandage, the dressing must be changed as needed or as instructed by your healthcare provider to maintain a clean wound environment that facilitates healing.
3. Eat a Balanced Diet
A healthy, nutrient-dense diet that is balanced in vitamins, minerals, and protein is an essential at-home wound care factor for supporting the body’s natural healing processes. Ensure you’re consuming an adequate amount of nutrients, including vitamin C, zinc, and protein, which play key roles in wound healing and tissue repair.
4. Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to stay hydrated and support optimal circulation and tissue hydration. Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining healthy skin and promoting wound healing from the inside out.
5. Follow Healthcare Provider’s Instructions
Adhere to any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding wound care, medication, and follow-up appointments. Attend all scheduled appointments for wound assessment and management and notify your healthcare provider if you experience any signs of infection or complications.
Signs or symptoms of infection can include redness, swelling, discomfort, increased temperature, or discharge at the site of the wound.
3 Things to Avoid As Your Wound Heals
1. Smoking
Smoking can impair blood flow, oxygen delivery, and immune function, all of which are crucial for wound healing. Avoid smoking or using tobacco products, as they can delay healing and increase the risk of complications and infections.
If you are a smoker and have a planned surgery, you will likely be asked to quit smoking a few weeks before surgery to help prepare your body for optimal healing. Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of postoperative complications.
2. Picking or Scratching the Wound
Resist the urge to pick, scratch, or manipulate the wound, as this can introduce bacteria, disrupt the healing process, and increase the risk of infection. If you know you may have difficulty not touching the site, it may be best to keep the wound covered with a dressing or bandage to prevent inadvertent irritation.
3. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption can impair immune function and interfere with the body’s natural healing processes. Limiting your intake of alcoholic beverages, especially during the initial stages of wound healing, will promote optimal recovery.
When to Seek Urgent Wound Care
If you care for your wounds without the support of in-home skilled nursing, ensure you monitor the appearance and symptoms associated with your wound. Improper wound care can lead to life-threatening conditions such as sepsis.
Taking pictures at least once a day is a great way to compare the day-to-day changes of your wounds. It also allows you to be able to send important images to your medical team so they can help.
People who require urgent medical attention may display the following symptoms:
- Unusual pain
- Excessive redness or swelling
- Warmth at the incision/wound site
- Large amounts of drainage or bleeding
- Foul-smelling discharge or wound site
- Fever
- Chills
If you observe any of these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Hire an In-Home Wound Care Specialist Near You
With the proper home health wound care and recovery assistance, wound healing can be expedited, or at least help you to avoid unnecessary complications.
Navi Nurses understands the needs of people coping with all types of wounds, and will closely collaborate with your current medical team to ensure that you heal as quickly as possible.
This is why we believe in providing holistic wound care at home, assessing your nutrition, sleep, and physical activity in addition to providing expert healthcare guidance — which are all key components of healing. With keen attention to the details of your physical assessment, Navi Nurses will be there to support you.
Heal properly on your terms — connect with our in-home wound care specialists for a holistic healing experience. Request on-demand care for yourself or a loved one today by calling us at (480) 482-1891 or reach out here. You’ll be heard by a medical professional right away.